Construction
Hidden Construction Compliance Costs That Catch Builders Off Guard | 9 Surprising Budget Busters
Most people think of concrete, bricks, and roofing when planning a build. They plan for labor, tools, and delivery fees. But many forget about the costs of following the rules. These are called construction compliance costs.
Compliance means following building laws. It includes permits, safety checks, and reports. These rules vary by country and even by town. They are not optional. If you break them, your project could stop.
In the US, you must meet strict fire and safety codes. In Canada, zoning and environmental laws can change your design. In the UK, planning permission is a long process. In Kenya, county approvals and NEMA reports are often missed. Each place has its own rules and hidden costs.
Builders often skip budgeting for these. That mistake can lead to big delays. It can also lead to fines or legal trouble. If you don’t plan for them, you may run out of money before the roof goes up.
This article explains the most common hidden costs. You’ll learn where they show up, what they cost, and how to avoid them. Whether you’re building a home or an office, this guide will help you plan better and save more.
🔍 What Are Compliance Costs in Construction?
construction compliance costs are the money spent to follow building rules. These rules come from the government, safety bodies, or local councils. They cover everything from permits to safety gear. You must pay them to start, run, and finish your project the right way.
These costs vary depending on your location and the size of your project. A small home and a large office block won’t face the same rules. But both must still follow the law. Skipping any part can lead to delays, fines, or a shutdown.
Many builders forget to plan for these costs. That leads to budget problems later. If you don’t know what to expect, you could lose time and money fast.
There are two types of compliance to understand. There are also two ways these costs show up in your budget.
📜 Regulatory vs. Voluntary Compliance
Regulatory compliance means rules you must follow by law. If you ignore them, your project could stop. Examples include building codes, fire safety rules, and zoning laws.
Voluntary compliance is not required. But it can improve your project. These include things like green building ratings or extra safety steps. They can make your building safer or more energy-efficient. They can also help you sell or rent it faster.
Even though voluntary rules are optional, many builders still choose them. Some buyers now expect energy-saving designs or better safety features.
💸 Direct vs. Indirect Compliance Costs
Direct costs are easy to see. These include permit fees, inspection charges, and safety equipment. You pay them upfront. You often get a receipt or license in return.
Indirect costs are harder to track. These may include time spent on paperwork, delays from missed approvals, or staff training. They still cost money. But you may not notice them right away.
For example, a delay while waiting for a permit is an indirect cost. You lose time and pay workers who cannot move forward. That loss adds up fast.
Both types of costs matter. If you only plan for the direct ones, the others will catch you off guard.
1️⃣ Building Permits and Inspection Fees
You can’t start a building project without a permit. Every country and city has its own rules. Whether you build a house or a shop, you must get the right papers first.
Permits allow the government to check your plans. They make sure your building is safe and legal. This protects both you and the public.
You also pay for inspections. Inspectors check the site at different stages of the build. They look at things like structure, wiring, plumbing, and fire safety.
These are some common permit and inspection costs:
Application fees
Plan approval charges
Reinspection fees if you fail the first check
Extra fees for fast-tracking
Renewal fees if the work takes too long
These costs are often higher in big cities. In some areas, they charge based on the size or value of your project. A bigger house or taller building means higher fees.
You may also need permits for small jobs. This includes adding a fence, changing a roof, or digging a borehole. Always check before you start. Doing work without a permit can lead to fines or a stop-work order.
In the US, permit rules differ by state and even by county. In Canada, you must follow your city’s building code. In the UK, local councils handle permits. In Kenya, each county has its own process through the physical planning office.
Failing an inspection can cost you more than the fee itself. You may have to redo work or call for another check. That adds delays and more labor costs.
Tip: Visit your local planning office before you draw your plans. Ask what fees apply. Knowing early helps you avoid surprises later.
2️⃣ Environmental Impact Assessments
You can’t start a building project without a permit. Every country and city has its own rules. Whether you build a house or a shop, you must get the right papers first.
Permits allow the government to check your plans. They make sure your building is safe and legal. This protects both you and the public.
You also pay for inspections. Inspectors check the site at different stages of the build. They look at things like structure, wiring, plumbing, and fire safety.
These are some common permit and inspection costs:
Application fees
Plan approval charges
Reinspection fees if you fail the first check
Extra fees for fast-tracking
Renewal fees if the work takes too long

These costs are often higher in big cities. In some areas, they charge based on the size or value of your project. A bigger house or taller building means higher fees.
You may also need permits for small jobs. This includes adding a fence, changing a roof, or digging a borehole. Always check before you start. Doing work without a permit can lead to fines or a stop-work order.
In the US, permit rules differ by state and even by county. In Canada, you must follow your city’s building code. In the UK, local councils handle permits. In Kenya, each county has its own process through the physical planning office.
Failing an inspection can cost you more than the fee itself. You may have to redo work or call for another check. That adds delays and more labor costs.
Tip: Visit your local planning office before you draw your plans. Ask what fees apply. Knowing early helps you avoid surprises later.
3️⃣ Health and Safety Compliance
Every job site must be safe. This is not optional. Safety rules protect workers and anyone near the site.
In the US, OSHA sets the standards. In the UK, it’s the Health and Safety Executive. Canada follows local safety codes. In Kenya, it’s the Directorate of Occupational Safety and Health Services.
You must follow safety laws from the first day. They cover things like working at heights, handling tools, and using machines.
Common safety costs include:
Safety officer wages
Hard hats, gloves, and boots
Safety rails and warning signs
First aid kits and fire extinguishers
Staff safety training sessions
If you skip these steps, you put people at risk. You also risk legal trouble. A serious injury can shut down your site. It can also lead to fines or lawsuits.
Some places require a safety plan before work begins. Others may ask for regular reports. You may also need safety drills for fire or accidents.
Small mistakes can cost big money. A missing helmet or a loose cable can lead to an accident. That accident can delay work for weeks.
Safety checks also take time. Inspectors may visit without notice. If they find a problem, they can stop all work.
Tip: Train your team before the first tool hits the ground. Safety starts with simple habits. Good habits save lives and protect your project.
4️⃣ Fire Safety Codes and Emergency Planning
Every building must meet fire safety rules. These rules save lives and protect property.
In the US, fire codes come from the NFPA. In the UK, the rules follow the Fire Safety Order. Canada has the National Fire Code. In Kenya, fire rules are set by local governments and the Fire Risk Reduction Rules.
You must plan for fires before construction begins. Fire safety is not something to fix later.
Common fire safety costs include:
Fire alarms and smoke detectors
Sprinkler systems and fire hoses
Fire-rated doors and walls
Exit signs and escape lighting
Fire drills and staff training
Emergency exits must be clear and easy to reach. Exit signs must stay lit at all times. In large buildings, you may need more than one route out.
Sprinklers and alarms must meet local standards. You may need a fire engineer to design the system. The system must be tested before use.
You also need a fire plan. This plan shows what to do in an emergency. It should be clear, simple, and posted where people can see it.
Failing a fire check can stop your project. Fixing fire problems later costs more. You may even have to tear down finished work.
Some buildings need extra features. Hospitals, schools, and malls must meet stricter rules. Always check what applies to your type of building.
Tip: Plan fire safety with your architect. It’s cheaper to design it in than fix it later.
5️⃣ Accessibility Requirements
Every building should be easy to use for everyone. This includes people with disabilities.
In the US, the law is called the Americans with Disabilities Act. In Canada, rules vary by province but follow similar goals. The UK uses the Equality Act. In Kenya, new buildings must follow the Persons with Disabilities Act.
Accessibility is not just about good design. It’s the law. If your building is not accessible, you may be fined. You may also be forced to make changes later.
Accessibility features may include:
Ramps instead of stairs
Wide doorways for wheelchairs
Grab bars in bathrooms
Elevators in buildings with more than one floor
Clear signs with large print or braille

You must think about these features from the start. Fixing them later is more expensive.
Some projects also need accessible parking and safe paths from the road to the door. Restrooms should have enough space to turn a wheelchair. Light switches and sinks should be easy to reach.
In public buildings like shops or schools, these features are required. In homes, rules may be softer, but adding them still helps.
Making your building easy to use helps everyone. It also shows respect and care for people’s needs.
Tip: Talk to your architect early. Ask them to include these features in the first design.
6️⃣ Zoning Law Compliance and Adjustments
Zoning laws control how land is used. They tell you what you can build and where.
Every city or town has its own rules. In the US, zoning laws decide if land is for homes, shops, or factories. In the UK, it’s called planning permission. In Canada, zoning bylaws are set by local councils. In Kenya, each county has zoning maps and codes.
You must check your land’s zoning before you design anything. If you build without checking, you could face fines. You might even be forced to stop or tear down your work.
Zoning laws can control:
What type of building you can put up
How close it can be to the road
How tall the building can be
How much open space you must leave
Parking spaces and access points
If your plan breaks a zoning rule, you need a change or special permit. This is called a zoning variance or amendment. It can take time and cost money.
Some places also have restrictions on colors, roof types, or fences. These rules protect the area’s look and use.
You may also face issues from neighbors. If your plan affects their view, light, or noise, they can object. That can delay your approval or lead to more changes.
Tip: Before you buy land, check its zoning. Ask what can be built there. Always get clear answers in writing.
7️⃣ Utility Hook-Up and Infrastructure Compliance
Every building needs power, water, sewer, and sometimes gas or internet. These services must follow set rules.
Before you connect, you must apply to each provider. You also need to pay connection fees. These fees vary based on your location and building size.
Common utility services include:
Electricity
Water supply
Sewer or septic systems
Gas lines
Internet and phone lines
Each service has its own process. Some require drawings or site visits. You may need to dig trenches or install meters. All work must meet the provider’s standards.
In some places, you must build part of the service line yourself. That can include pipes, poles, or cables. This work adds cost and time to your project.
In rural areas, services may be far away. You may need to pay more to reach the nearest line. In cities, the cost may include road cuts, permits, or traffic control.
Hidden costs include:
Permit fees for trenching or drilling
Inspection charges
Equipment rental
Delays while waiting for approvals
Some countries also require water tanks, solar systems, or backup generators. These rules depend on local laws or grid strength.
Tip: Contact all utility companies before you start building. Ask what they need. Plan for delays or extra steps.
8️⃣ Documentation and Legal Construction Compliance Costs
Every building project comes with a pile of paperwork. You can’t skip it or rush it.
Before you build, you need drawings and approvals. During construction, you must keep records. After you finish, you must show proof that you followed the rules.
Common documents include:
Site plans
Floor plans
Structural drawings
Land ownership papers
Survey reports
Soil tests
You may also need letters from architects or engineers. These letters confirm that your design is safe and meets the law.
In many places, you must hire a lawyer to review land records. This helps avoid fraud or land disputes. It also ensures your land is free of claims or court orders.
Some towns or cities require digital copies of every file. Others want printed versions with stamps and signatures. Each place has its own rules.
Missing or wrong papers cause delays. You may have to pay fines or redo work. This wastes both time and money.
Other hidden costs include:
Consultant fees
Notary services
Filing charges
Copying and printing
Extra time waiting for approval
If your project changes midway, you must update your paperwork. Even small changes need new stamps or signatures.
Tip: Keep all records safe and backed up. A missing document can stop your whole project.
9️⃣ Delays Due to Non-Compliance
Missing a rule can stop your project cold. It doesn’t matter how far along you are.
When inspectors find a mistake, they may issue a stop-work notice. You must fix the issue before work can continue.
Delays can last days or even months. It depends on how fast you correct the problem and get approval again.
Common causes of delays include:
Missing permits
Unapproved changes to the plan
Poor quality materials
Unsafe working conditions
Ignoring local laws
Each delay adds cost. Workers wait. Equipment sits unused. Your timeline stretches.
In some places, you must pay fines before work can restart. You might also need a new inspection, which can take time to schedule.
Banks and investors may lose confidence if delays pile up. They may pause funding or pull out.
Delays can also upset neighbors. This can lead to more reports or legal trouble.
Tip: Follow every rule from the start. Ask questions if you are not sure what’s required.
💡 How to Budget for Compliance from Day One
🧠 Hire a Compliance Consultant
They:
Know local laws
Identify risks early
Save you costly mistakes
In Canada and the UK, they’re called compliance officers or project consultants. In Kenya, you can hire a registered architect or planner.
📲 Use Compliance Management Software
Options include:
Procore (USA/Canada)
PlanRadar (UK/EU)
ArchiCAD or AutoCAD tools (Kenya)
They help keep track of documents, deadlines, and inspections.
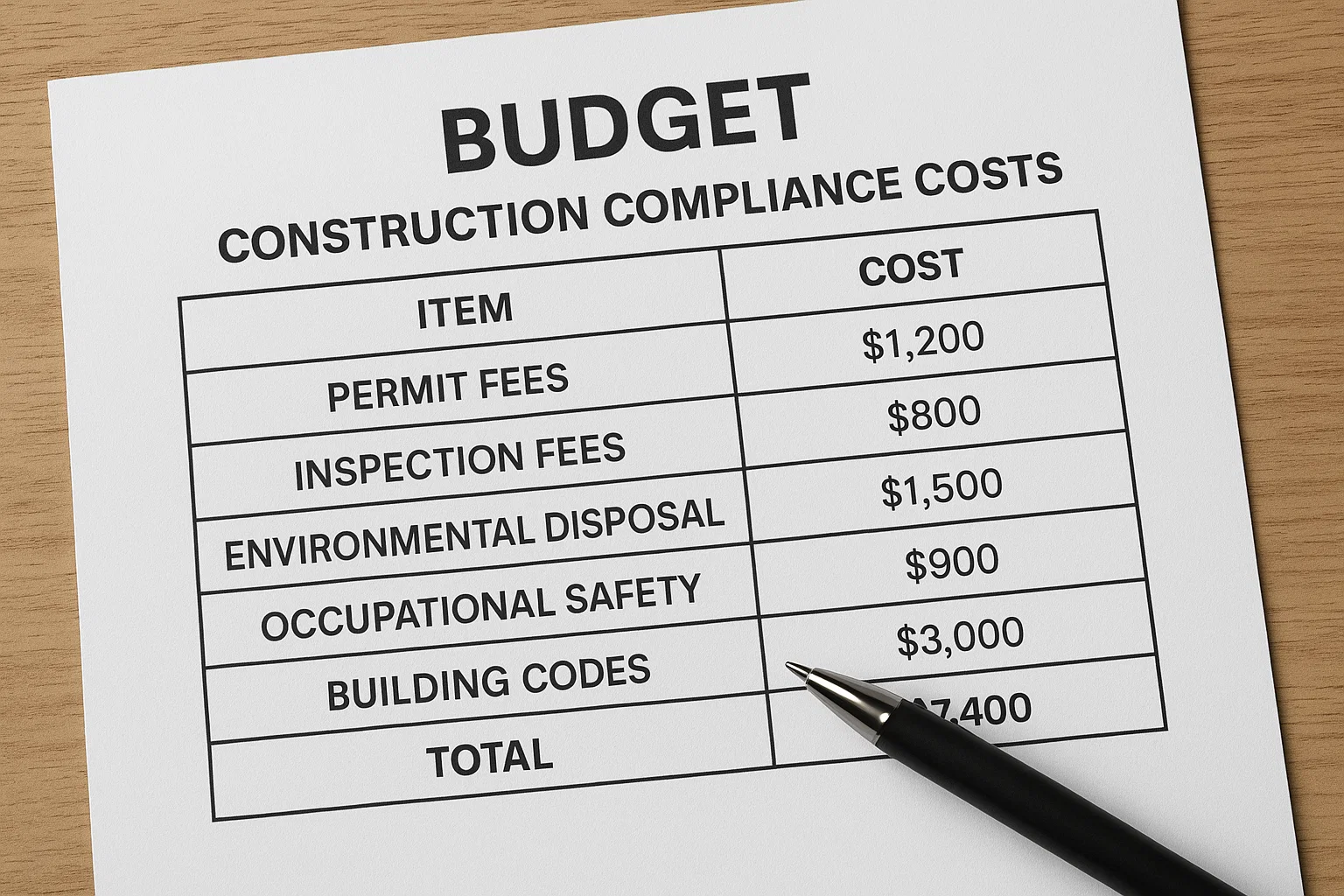
🌍 Real-Life Examples from the US, UK, Canada and Kenya
Texas, USA: A school project was delayed 6 months due to missing fire egress design, costing $200,000 in labor and penalties.
Ontario, Canada: A duplex needed rezoning mid-project, triggering a $40,000 redesign and 2-month delay.
Manchester, UK: Contractor fined £10,000 for failing to provide disabled access on a retail fit-out.
Kisumu, Kenya: A developer ignored EIA licensing. Project halted by NEMA. Losses exceeded Kshs. 1.5 million.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Are construction compliance costs the same in every country?
No. They vary based on national and local regulations. For example, the US and UK have stricter environmental rules than Kenya, but Kenya has unique county-specific laws.
2. Can I avoid any of these construction compliance costs?
No. Skipping compliance exposes you to legal action, fines, and project shutdowns. You can reduce costs by planning ahead and working with experienced professionals.
3. Is compliance more expensive in cities or rural areas?
City areas often have more regulations, but rural areas may require expensive utility setups and infrastructure.
4. Do residential and commercial projects face the same costs?
Commercial buildings usually face stricter fire, safety, and accessibility standards, hence higher construction compliance costs.
5. Who should manage compliance on my project?
Either hire a certified compliance consultant or partner with a firm that understands your local laws and requirements.
6. How do I know if I’m compliant?
Check with your local building authority, consult a licensed architect or planner, or use project compliance tools to audit your progress.
🏁 Conclusion: Build Smart with Nyolenju Structures
Whether you’re building in the US, Canada, the UK, or Kenya; compliance is non-negotiable. The real cost of ignoring regulations is much higher than doing things right from the start.
Nyolenju Structures Limited provides expertly crafted building plans that meet all required codes, from local zoning laws to fire and safety standards. Our designs are tailored for hassle-free approvals; saving you time, money, and stress.
Avoid nasty surprises. Build with confidence.
✅ Choose Nyolenju Structures for code-compliant building plans.
📞 Call or WhatsApp Nyolenju today to get started.

